How Mold Affects Pets
Mold produces spores that can become airborne and inhaled or ingested by pets. These spores can trigger a range of health problems, especially for animals with weaker immune systems, pre-existing respiratory conditions, or prolonged exposure to mold.
Symptoms of Mold Exposure in Pets
Pets exposed to mold may show symptoms such as:
-
Respiratory Issues: Coughing, sneezing, wheezing, or difficulty breathing.
-
Allergic Reactions: Excessive scratching, skin irritation, or redness.
-
Digestive Problems: Vomiting, diarrhea, or loss of appetite.
-
Lethargy: Reduced energy levels or unusual tiredness.
-
Behavioral Changes: Anxiety, agitation, or restlessness.
If your pet displays any of these symptoms and you suspect mold exposure, consult a veterinarian promptly.
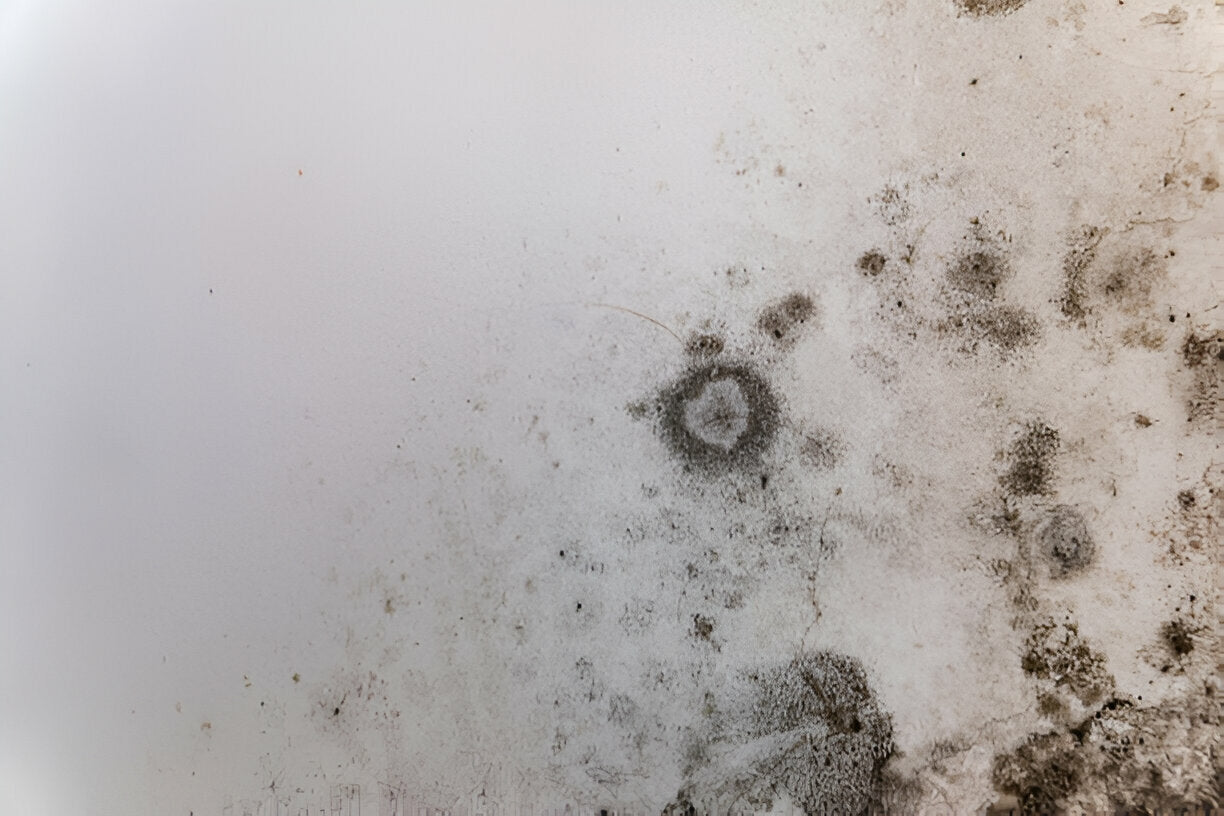
Types of Mold Harmful to Pets
While all molds can potentially cause issues, certain types are particularly harmful to pets:
-
Black Mold (Stachybotrys chartarum): Known for its toxicity, black mold can cause severe respiratory and neurological problems in pets.
-
Aspergillus: Commonly found in damp areas, this mold can lead to aspergillosis, a respiratory infection that affects pets and humans alike.
-
Cladosporium: This mold can cause skin and respiratory irritation in pets.
Common Sources of Mold in the Home
Mold thrives in damp and humid environments. Common areas where mold might develop include:
-
Bathrooms and kitchens
-
Basements and crawl spaces
-
HVAC systems and vents
-
Leaky roofs or windows
-
Pet bedding or food stored in humid conditions
How to Protect Your Pets from Mold
-
Identify and Eliminate Mold: Regularly inspect your home for signs of mold, especially in high-risk areas. If you find mold, address the source of moisture and remove the mold promptly.
-
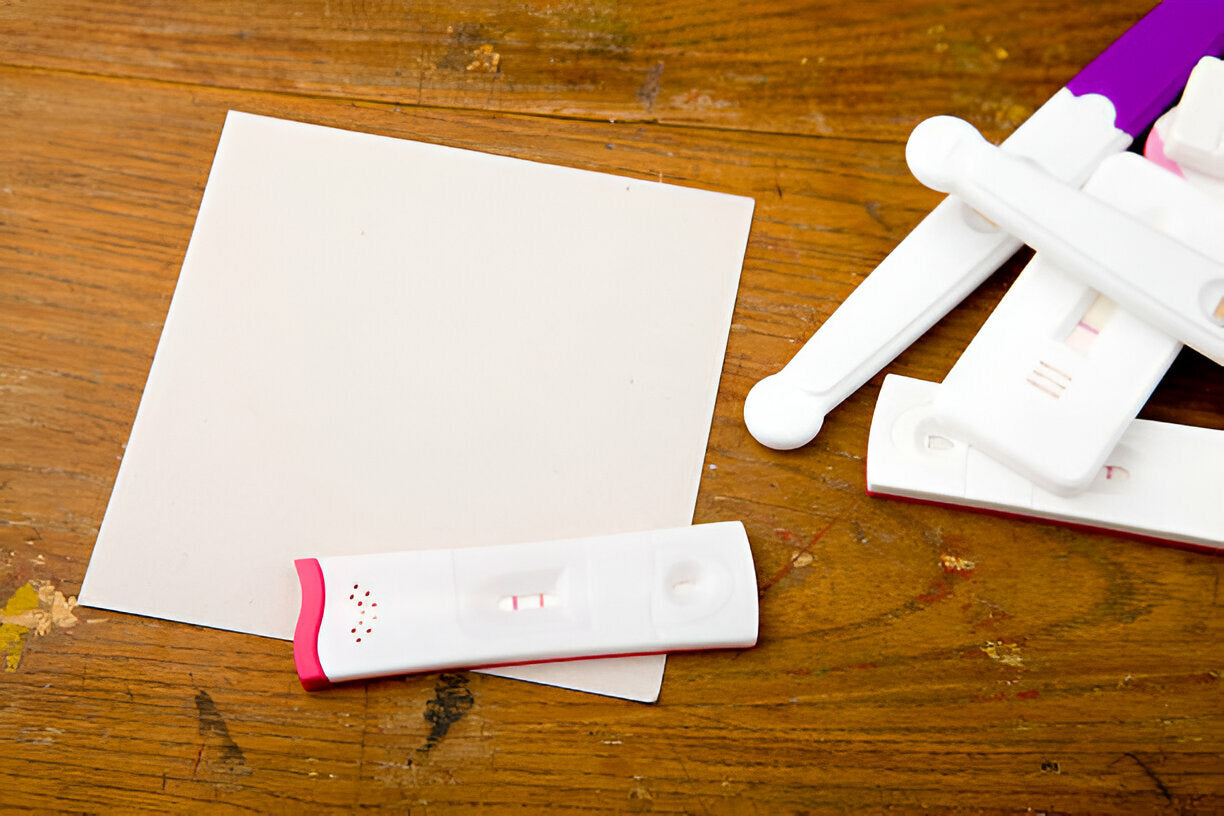
Use a DIY Mold Testing Kit: To ensure your home is safe, consider testing for mold using a professional-grade DIY kit. These kits allow you to detect mold presence without hiring a professional.
-
Improve Ventilation: Ensure your home is well-ventilated to reduce humidity levels, particularly in areas like bathrooms, kitchens, and basements.
-
Maintain Pet Areas: Keep pet bedding, toys, and feeding areas clean and dry to minimize mold growth.
-
Use Dehumidifiers: In humid climates, a dehumidifier can help maintain ideal indoor moisture levels to prevent mold growth.
What to Do If Your Pet Is Exposed to Mold
-
Consult Your Veterinarian: If you suspect your pet has been exposed to mold, seek veterinary care immediately. Be prepared to describe the symptoms and any known mold exposure.
-
Remove Your Pet from the Affected Area: Relocate your pet to a clean, mold-free environment while addressing the mold problem in your home.
-
Clean and Sanitize: Wash your pet’s bedding, toys, and other belongings thoroughly to remove any mold spores.
-
Address the Mold Problem: Use professional-grade mold testing kits to identify the extent of mold contamination, and seek remediation if necessary.
How to Test for Mold Exposure in Pets
Pets, like humans, can suffer from mold exposure, which may lead to respiratory issues, allergies, or other health problems. Identifying mold-related illnesses in pets involves recognizing symptoms, consulting a veterinarian, and possibly testing for mold exposure. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to test for and address mold exposure in pets.
Step 1: Recognize the Symptoms of Mold Exposure
Mold exposure can manifest in pets through various symptoms, including:
-
Respiratory Issues: Coughing, sneezing, difficulty breathing, or wheezing.
-
Allergic Reactions: Skin irritation, excessive scratching, or redness.
-
Digestive Problems: Vomiting, diarrhea, or loss of appetite.
-
Behavioral Changes: Lethargy, restlessness, or increased anxiety.
-
Neurological Symptoms: Tremors or seizures (in severe cases).
If you notice any of these symptoms, particularly after suspected mold exposure, it’s essential to take action promptly.
Step 2: Visit a Veterinarian
Consulting a veterinarian is critical for diagnosing and treating mold exposure. The vet will likely:
-
Conduct a Physical Examination: To assess your pet's overall health and identify any physical signs of mold exposure.
-
Take a Detailed History: Provide information about your pet’s environment, including any potential mold exposure in your home, bedding, or outdoor areas.
-
Order Diagnostic Tests:
-
Blood Tests: To check for elevated immune responses, inflammation, or mold toxins.
-
Urinalysis: To detect signs of infection or toxins in the system.
-
X-rays or Imaging: To examine the respiratory system for signs of mold-related damage, such as pneumonia.
-
Allergy Testing: To determine if your pet has developed sensitivities to mold spores.
-
Step 3: Environmental Mold Testing
Testing your home for mold is equally important to confirm the source of exposure. This can be done with:
-
DIY Mold Testing Kits: Professional-grade mold testing kits allow you to collect surface samples and send them to a lab for analysis.
-
Professional Mold Inspection: If you suspect a severe mold problem, consider hiring a mold inspector to assess and address the issue thoroughly.
-
Pet-Specific Areas: Focus on areas your pet frequently visits, such as bedding, feeding stations, and play areas, to identify hidden mold sources.
Step 4: Remove Mold from Your Home
To prevent further exposure, take steps to eliminate mold from your home:
-
Clean Affected Areas: Use mold-removal solutions on non-porous surfaces and discard heavily infested materials, such as pet bedding or toys.
-
Control Moisture: Reduce humidity levels in your home with dehumidifiers and fix leaks promptly.
-
Improve Ventilation: Ensure proper airflow in damp areas like bathrooms, basements, and kitchens.
-
Wash Pet Items Regularly: Clean and dry your pet’s bedding, toys, and food dishes frequently to prevent mold growth.
Step 5: Follow Veterinarian’s Recommendations
After diagnosis, your veterinarian may prescribe treatments such as:
-
Medications: Antihistamines, anti-inflammatory drugs, or antibiotics for infections.
-
Supportive Care: Oxygen therapy or hydration for pets with severe symptoms.
-
Environmental Adjustments: Recommendations to improve your pet’s living conditions and prevent future exposure.
Prevention Tips
-
Inspect your home regularly for signs of mold, especially in damp or humid areas.
-
Maintain a clean and dry environment for your pet.
-
Use air purifiers with HEPA filters to reduce airborne mold spores.
-
Test your home for mold periodically, especially if your pet has ongoing health issues.
Final Thoughts
Mold exposure can pose significant risks to your pet’s health, but early detection and proper care can make a big difference. By staying vigilant about symptoms, consulting a veterinarian, and maintaining a mold-free environment, you can keep your furry friends safe and healthy.